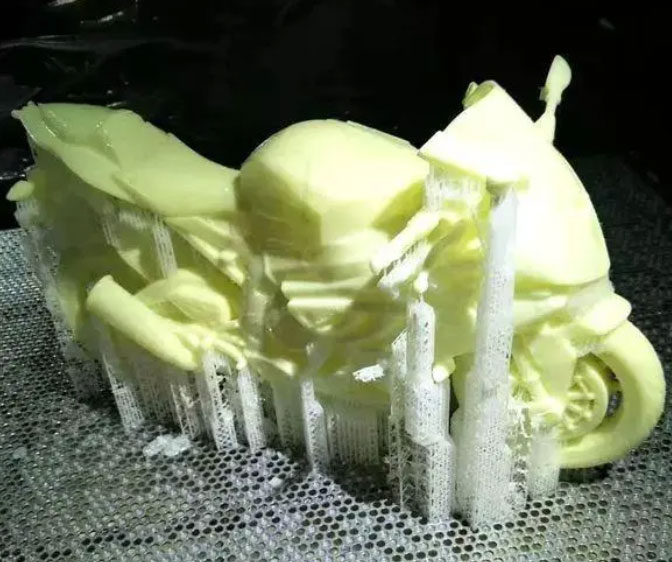
CNC Machining and 3D Printing each have their own unique advantages. Considering cost and availability, you may want to use them in different situations. Now, let us find out their differences and advantages to find out which one is right for your prototype.

- Working principle
SLA
SLA is an industrial 3D printing or additive manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled lasers to manufacture parts in UV-curable photopolymer resins. Use a laser to track and cure the designed cross section of the part on the surface of the liquid resin. Then lower the cured layer below the surface of the liquid resin and repeat the process. Each newly cured coating is attached to the coating below it. This process will continue until this part is completed.
SLS:
It is also a 3D printing method. In the SLS process, a computer-controlled carbon dioxide laser sucks nylon powder from bottom to top onto a hot bed, where the powder is gently sintered (fused) into a solid. After each layer, the rollers put a new layer of powder on the bed and repeat the process.
CNC machining:
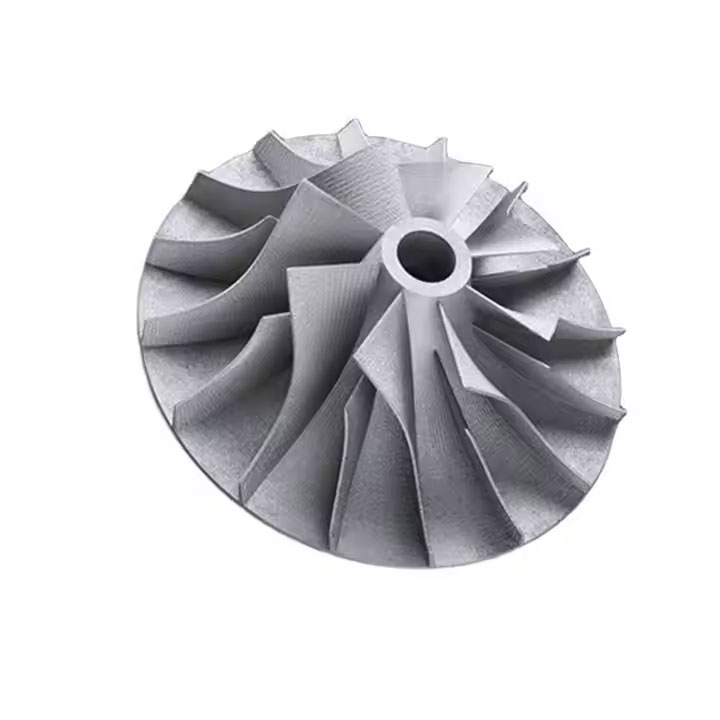
CNC machining starts with a piece of material and uses a rotating tool to shape it. Following this procedure, it cuts off the excess part until you get the finished product. - Material usage of CNC and 3D printer
SLA: Thermoplastic-like photopolymer
These resins are not as strong as engineering grade plastics, so parts made with SLA have limited use in functional testing.
SLS: Nylon, TPU
SLS parts are more durable than SLA parts, but there are limited resin options.
CNC: Most commodity and engineering grade thermoplastics and metals
CNC machining work with various materials. Can be used for: ABS, ABS+PC, polycarbonate, polycarbonate, acrylic, nylon, PP, PA6+GF30%, POM, PE, TEFLON, PEEK, PPE, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, copper, bronze, brass, Wood, glass, Corian, etc.
Generally speaking, CNC machine tools are more suitable for prototypes that can withstand structural testing because they engrave designs from target materials. Structural tests and changes will be more accurate because they use target materials. - Accuracy level
CNC Machining is more precise and consistent than 3D printing because they have higher heat resistance. When the temperature is too high, the 3D printer will produce deformed products.
CNC machine tools do not heat and modify materials. Compared with 3D printers, this material has better strength and structural integrity, because 3D printers need to heat this material to produce the desired product. - Surface finish
3D printed parts have grainy or sandy texture.
CNC machine tools provide a better surface finish than 3D printing because the material will not be deformed during processing. The rigid material and cutting action keep the product together, reducing the chance of error or deformation. - Speed
3D Printing and CNC machining are both rapid prototyping methods. They can produce parts within days or even hours.
If you need to finish machining your product, CNC machining can be easier and faster because the surface is already quite smooth. 3D printed products require a lot of cleaning and polishing work after they are finished.
6.Geometric restrictions
3D printing can produce parts with complex geometries. However, 3D printers can only use the area of the print bed to manufacture parts, so large parts may not fit this space.
There may be some geometric limitations and CNC machining. Because CNC machining is a subtractive process, milling can sometimes be tricky.